Now a celebration to honor the office of the president of the United States, President’s Day was originally a celebration of George Washington’s birthday; Washington, the hero of the War for Independence and our nascent republic’s first president. An equally familiar image of Washington is the boy who could not tell his father a lie. Familiar to all, but what are the origins of this universally known presidential anecdote?
In the Early American Republic no public figure was more universally revered than George Washington. Shortly after his death in 1799 M.L.(Parson) Weems wrote a small, single-volume biography of Washington, The Life of George Washington: with curious anecdotes, equally honorable to himself, and exemplary to his young countryman. Focused primarily on the young Washington, the book was an effort to humanize a public man for mass consumption and provide an instructive model of virtuous behavior.
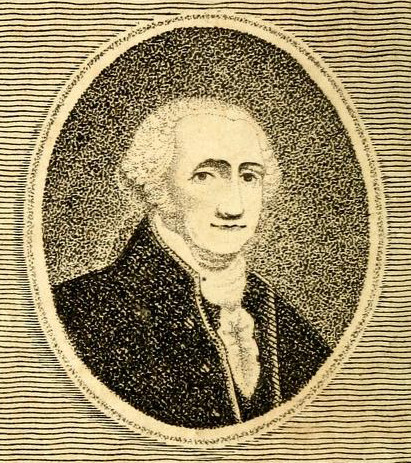

Among the many colorful vignettes from Weems’s Life is the story of a young Washington, hatchet in hand, unable to lie when confronted by his father over a felled cherry tree. Weems attributed the story to an “aged lady” who spent time on the Washington family farm.

Despite criticism from contemporary gentlemen such as John Adams and Chief Justice John Marshall (who, perhaps not coincidentally, wrote his own 5-volume biography of Washington) the book was immensely popular. A New York Times best-seller of its day, it went through 29 editions in its first 25 years of publication.
Live virtuously this President’s Day!
Post contributed by Joshua Larkin Rowley, Research Services Coordinator.