By Blake Hill-Saya

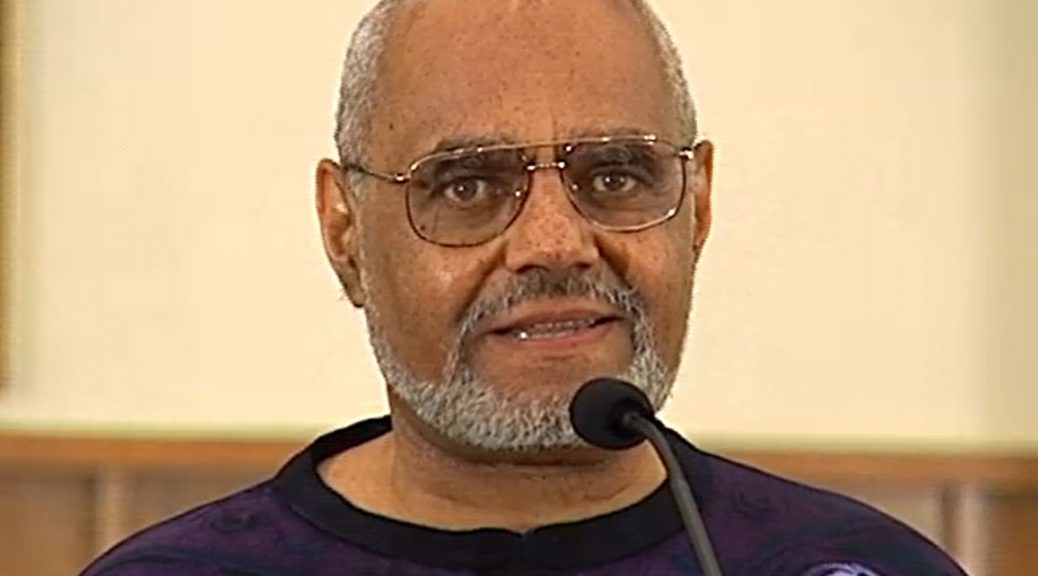
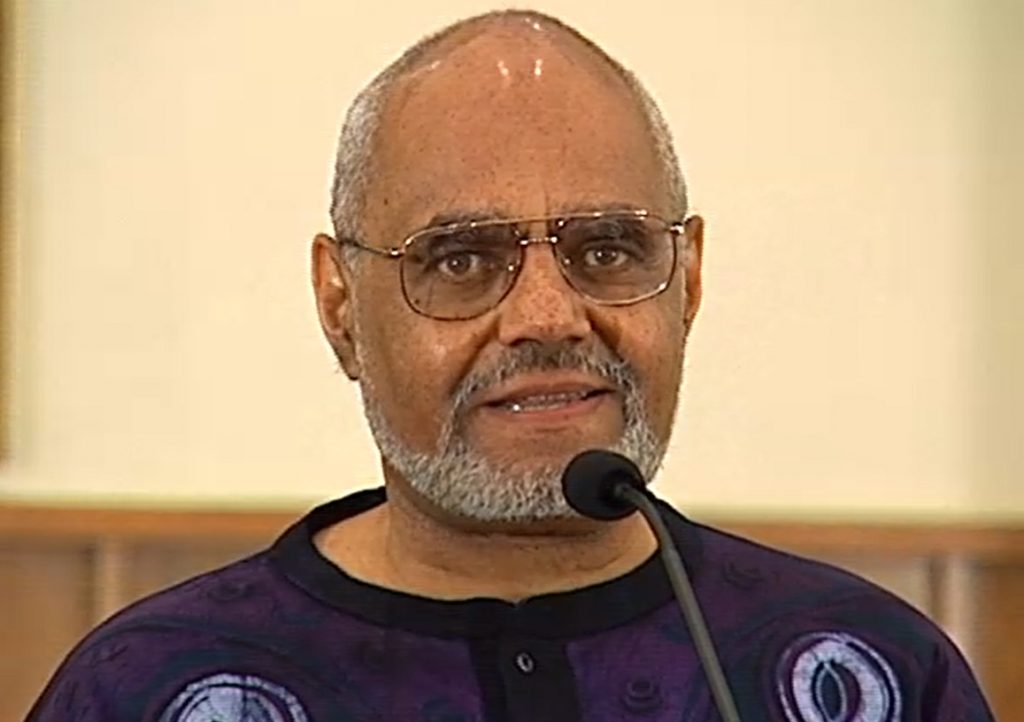
Above: Portrait in oils of Dr. Aaron McDuffie Moore painted by his daughter Lyda Moore Merrick. Located in the North Carolina Collection, Stanford L. Warren Branch of the Durham County Library, Durham, N.C.
Too often we relegate the lives of our ancestors to the basket of nostalgia. We think that because our modern times have dressed us up in different clothes and surrounded us with technology that the lives and struggles of our ancestors can’t speak with any real directness to ours. It is easy in the rush and rattle of the present to allow seasoned historians to define us in macrocosm while overlooking the importance of our own more granular history; a thread waiting to be pulled in the warp and woof of who we think we are. Libraries and historical archives exist to help us pull that thread and expand our understanding of history and our place in it.
Eight years ago, I was chosen by the Durham Colored Library board of directors, led by chairperson C. Eileen Watts Welch, to follow my own ancestral thread and write a biography of my great- great-grandfather, Dr. Aaron McDuffie Moore. The dream of this historical biography of Durham’s first Black physician far predates my involvement; it actually predates me. Dr. Moore’s daughter, my great-grandmother, Lyda Moore Merrick, dreamed of a book about her Papa. My grandfather, Dr. Charles DeWitt Watts, a legendary surgeon and healthcare activist in his own right, also dreamed of this book. His dream inspired his daughter, C. Eileen Watts Welch, to make this biography a reality. The Durham Colored Library, an organization founded by Dr. Moore himself in 1913 and now a non-profit focused on uplifting Black narratives, sponsored the project.
The Rubenstein Rare Book & Manuscript Library was the first of many such archives that I would find myself exploring on my journey. The hallowed feeling of that space and the respect with which my ancestral papers are cared for there was in and of itself a revelation. Black history is not, in my experience, often afforded this level of protection or gravitas. Having to make a reservation to review things I remember first seeing on my grandfather’s desk years ago was very emotional for me. One document discovery I made, however, vividly illustrates the importance of these archives.
Several years into my research, I was cross-referencing the papers of Dr. Moore’s contemporaries to glean any possible mentions of him. One day, in Charles Clinton Spaulding’s papers, (Dr. Moore’s nephew and another member of Durham’s “Mighty Triumvirate” along with John Merrick) I noticed a file labeled “Anon. memo book.”[1] I am based in Los Angeles, so I asked my research partner (and aunt) C. Eileen Watts Welch if she had time to go and see what it was. When she finally found it, it took her breath away.

In her hand was a brown leather-bound doctor’s visiting book from Dr. Aaron McDuffie Moore’s first year of practice in Durham (1888-1889). She could actually feel the imprint of his fingers in the leather. She called to tell me. We both cried. She told me it even smelled sort of earthy and sweaty and maybe even like the saddlebags of the horse he rode on his rounds. Together we had unearthed the Rosetta Stone of Black healthcare in Durham.

The entries start neatly and sparsely and, as the year goes on, the pages fill to the brim. Payments are often recorded as produce, a basket of eggs, a dollar here and there. He is attending to everything from burns and pellagra to child birth and gunshot wounds. His stress level and commitment are visible in the pressure of his pencil on the paper. This miraculous connection was made possible because the Rubenstein Library cared enough to preserve, itemize and digitally list this precious artifact. I will be forever indebted to C. C. Spaulding, the NC Mutual Life Insurance Company’s staff and archivists through the years, and every librarian and archivist who made sure that, 129 years later, his ancestors would get to feel the imprint of his fingers in his visiting book.
Archives and historical collections have the power to heal, inspire and affirm the many diverse threads in the fabric of our national tapestry. History includes all of us.
I hope our adventure sparks the beginning of yours.


Aaron McDuffie Moore: An African American Physician, Educator and Founder of Durham’s Black Wall Street by Blake Hill-Saya is available from UNC Press and can be found wherever books are sold. Contact The Durham Colored Library for official autographed copies.
[1] This item was previously identified as “Anonymous memo book.” Due to Blake Hill-Saya and C. Eileen Watts Welch’s research, the Rubenstein Library was able to rename the description for this item. It can now be found as, Dr. Aaron McDuffie Moore doctor’s visiting book, Charles Clinton Spaulding papers, 1889-1990, David M. Rubenstein Rare Book & Manuscript Library, Duke University.