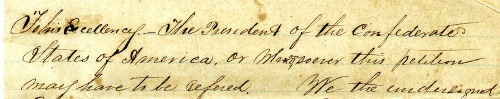Working on the History of Medicine (HOM) Trent Manuscripts Grant Project has revealed quite a few items of interest—but most recently, I discovered something that fits rather well into the Memories of the Civil War exhibit currently on display in the Perkins Exhibit Gallery.

You may have seen the grisly amputation kit from the HOM collection, which might be the kind of war-related artifact that you would expect out of a collection on the history of medicine. But here, instead, is not an example of progressive advances in medicine, nor a relic of past practice: instead, a simple plea for a family doctor to remain in service to his community by being excused for service in the Confederate Army:
“We the undersigned Citizens of Cripple Creek, Wythe County, VA earnestly petition that our family physician, Dr. C. C. Campbell, who is a conscript under the late act of Congress and whose services are indispensable to this portion of the county, be exempt, or detailed, and left with us.”
This singular petition to the President of the Confederacy, Jefferson Davis, dated February 15, 1864, was accompanied by two pages of signatures by the residents of Cripple Creek. Did it ever reach its destination? Do any historians or local residents know the fate of Dr. C. C. Campbell and his patients in Cripple Creek, Virginia? If so, we’d love to hear from you!
Jacqueline Chapman, a graduate student at UNC-Chapel Hill’s School of Information and Library Science, was History of Medicine Intern at the Rubenstein Library from September 2011 to January 2012.