It’s the fourth Friday of the month, so it’s time for another trip to the Rubenstein Library Test Kitchen!
As an intern in the University Archives, I determined to find a recipe from among the University Archives collections for my Rubenstein Library Test Kitchen post. I settled on one from a cookbook in the Law Dames records. The Duke Law Dames was a social and service organization in the 1950s-1970s made up of primarily law student wives, but it was also open to women law students and wives of faculty and alumni. The group helped new members settle into the Durham area and offered social and educational events such as lectures, cooking demonstrations, and parties. As the spouse of a Duke graduate student, I identified with the Law Dames’ aims to welcome new arrivals and provide a community of support (although no group cookbooks or fashion shows for me).

Culinary Casebook was published in 1972. The cover (clever artwork!) is worn and has a few stains, and there are pencil marks within: page numbers written in the title page, checkmarks next to some some of recipes. I think this book was well-loved and well-used. It includes front matter about ingredient substitutions, meal planning, herb, meat and sea food guides, and some diet and nutritional information. Reminding me of an almanac, there is also a section of miscellany: symptoms and prevention of common illnesses, first aid tips, planting charts, Bible verses, how to determine the date of Easter. Why can’t I find that in today’s cookbooks?
As a vegetarian, my selection was somewhat limited but I still had a hard time deciding which recipe to try. The successful Velveeta Corn Ring from an earlier post made me more bold and adventurous than I might have otherwise been, and I settled on something that sounded a bit strange and piqued my curiosity: Tomato Soup Cake.

Tomato Soup Cake
1 can tomato soup
1tsp. soda
¼ c. cream
Dissolve soda in soup and let stand a few minutes. Take another bowl and put in:
1 c. sugar
1 heaping Tbsp. Spry
1 pinch salt
Mix well, then add both mixtures together, then add:
2 c. cake flour
1 tsp. baking powder
1 tsp. cinnamon
½ tsp. cloves
(Sift twice before adding.) Mix well and add:
½ c. raisins, floured
1 tsp. lemon extract
Bake 1 hour in slow oven in bread pan 9x5x2 ½ inches deep – 10 minutes at 350 degrees, 50 minutes at 325 degrees.

I’m not a method historical cook, so I resorted to using my stand mixer. More power to you though if you want to use the old-fashioned bowl and spoon. The recipe does not specify if the tomato soup should be condensed or not but since condensed tomato soup is the most ubiquitous that’s what I used, reasoning I could always add a can of water later if the batter looked too dry. It came out perfectly though with just the condensed soup.
I come from a “pop” not a “soda” kind of family, but my first reaction was to think there was some kind of carbonated beverage in the bread. The recipe is, of course, referring to baking soda. As anyone with some knowledge of chemistry might have guessed, when I stirred the baking soda into the soup it reacted to create a nice, fluffy, fizzy kind of mixture. I’m not much of a chemist, so this surprised me!
I hadn’t heard of Spry before. A quick Google search told me it was a brand of vegetable shortening, so I substituted Crisco. Interestingly Spry’s popularity waned after the 1950s, which makes me wonder if the recipe originated at least twenty years before its publication in the Law Dames cookbook. A little online browsing reveals a general consensus that tomato soup cake originated in the early twentieth century prior to World War II.
I didn’t have cake flour on hand and couldn’t find it on my grocery trip, so I found a substitution: for each cup, use all-purpose flour and replace two tablespoons of it with cornstarch.
I assumed that the cloves called for were ground cloves. I also forgot to sift together the powdered ingredients. So much for reading the recipe beforehand! Actually I had, but I was too caught up in the drama coming together in my mixing bowl.
 I put the batter in a greased 8.5 inch pan and baked for an hour as instructed. I ended up leaving it in for an additional fifteen minutes, but chalk it up to the peculiarities of my oven. The smell of cinnamon and cloves reminded me of pumpkin bread or some other kind of spicy, wintry baked deliciousness. Very appropriate for these chilly January days.
I put the batter in a greased 8.5 inch pan and baked for an hour as instructed. I ended up leaving it in for an additional fifteen minutes, but chalk it up to the peculiarities of my oven. The smell of cinnamon and cloves reminded me of pumpkin bread or some other kind of spicy, wintry baked deliciousness. Very appropriate for these chilly January days.
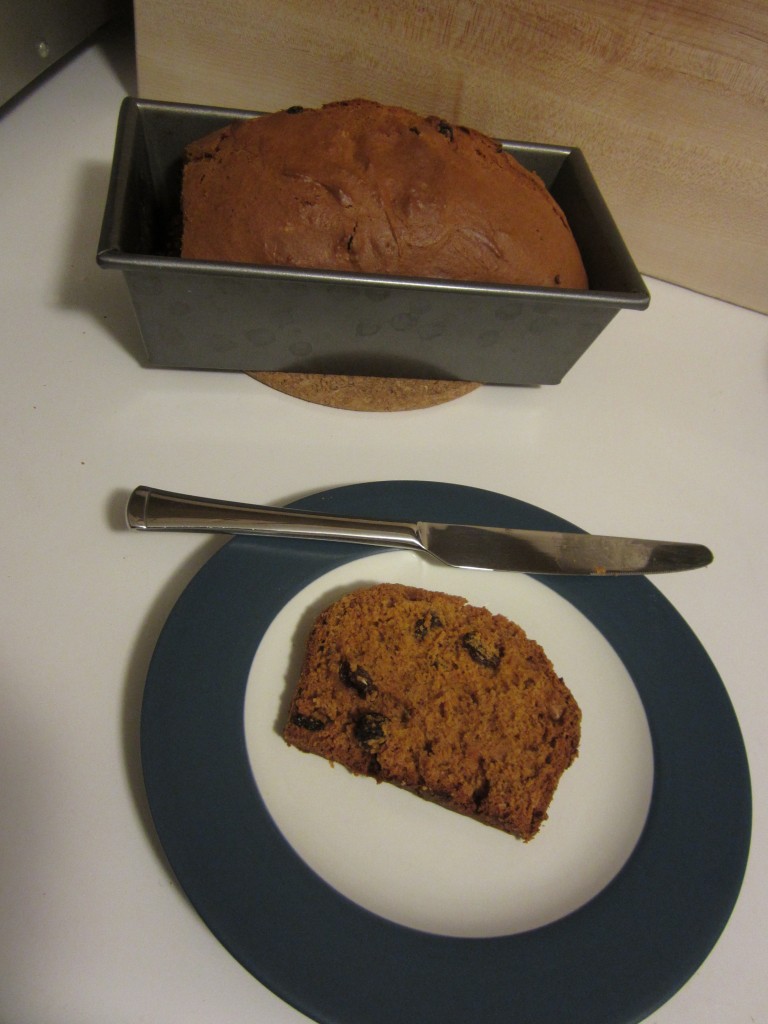

The cake emerged looking and smelling more like a quick bread than a cake to me; I’m not entirely sure if that’s how it’s supposed to be or if it’s because I used all-purpose flour. Either way, it was delicious. The mild, faintly tart flavor mixed well with the raisins and spices. Warmed up with a bit of butter, it made a great breakfast, snack, or dessert. I would give it five stars!
When considering historical recipes, perhaps most people think of time measured in centuries, not decades – I know I do. Yet the pace of change can be very fast; it’s interesting to note what has changed and what has not in forty years. Assumptions about common knowledge or available ingredients shift over time, and something that sounds normal at one time seems strange at another – I didn’t know what to expect from tomato soup cake. But the Law Dame who submitted this recipe knew what she was doing! Here’s to trying something (old?) new
Post contributed by Jamie Burns, Isobel Craven Drill Intern, University Archives









 I put the batter in a greased 8.5 inch pan and baked for an hour as instructed. I ended up leaving it in for an additional fifteen minutes, but chalk it up to the peculiarities of my oven. The smell of cinnamon and cloves reminded me of pumpkin bread or some other kind of spicy, wintry baked deliciousness. Very appropriate for these chilly January days.
I put the batter in a greased 8.5 inch pan and baked for an hour as instructed. I ended up leaving it in for an additional fifteen minutes, but chalk it up to the peculiarities of my oven. The smell of cinnamon and cloves reminded me of pumpkin bread or some other kind of spicy, wintry baked deliciousness. Very appropriate for these chilly January days.