The Assessment & User Experience department at Duke University Libraries keeps the libraries’ physical and virtual spaces responsive to user needs by constantly gathering feedback. In additional to our biennial user satisfaction survey, we run usability tests, hold focus groups, and host meetings of our student advisory boards, all in an effort to keep a finger on the pulse of the DUL patrons.
These activities can generate a lot of unstructured data! For example, in a typical meeting of our undergraduate advisory board, we might collect feedback from a dozen or more students, generating seven or more pages of notes and covering a range of topics. We review and act upon some of these comments immediately, but others may influence longer-term planning. As library staff, we know how important it is to store information in a way that promotes future access. This year we decided to pilot a new system for storing and describing our unstructured data.
 Enter Airtable. If you’re not familiar, Airtable is a cloud-based database solution. Similar to Google Sheets, Airtable lets you enter and share data in your web browser, but it also offers more powerful features for projects that have messy data or interconnected components. There are many Airtable templates to show off the different features, including project trackers, event planners, and even product catalogs.
Enter Airtable. If you’re not familiar, Airtable is a cloud-based database solution. Similar to Google Sheets, Airtable lets you enter and share data in your web browser, but it also offers more powerful features for projects that have messy data or interconnected components. There are many Airtable templates to show off the different features, including project trackers, event planners, and even product catalogs.
For our messy data, we built a simple spreadsheet that was general enough to collect data from a variety of sources. We included columns like basic demographics, the feedback provided, the original question or prompt, the date when feedback was provided, and how we collected the feedback. Then we took advantage of Airtable’s special features to create a column for topical tags. One of the column types in Airtable is called “multiple select“, which means you can add multiple tags to a single comment. Other spreadsheets can’t understand a list of tags in a single cell, but Airtable treats each tag separately and allows us to group and filter comments by each individual tag.

The ability to look at comments across different feedback channels in one central location has enormous potential. Instead of having to hunt through old Word documents or emails, we have a single database that can be searched, sorted, or filtered to explore trends in comments over time. When a question comes up about how patrons feels about a particular service or space, we can compile data much more easily, and we no longer have to rely on our memory of what feedback we’ve received and when.
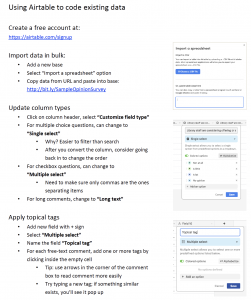
Airtable’s free accounts have a limited number of rows allowed in each database, but they do offer a discount on paid plans to educational institutions. We’re only just starting to explore the potential of Airtable, but so far we’ve been happy with the ability to collect our messy data in one place and organize comments with tags.
Want to learn more? Take a look at our recent tutorial on using Airtable for coding survey data, originally offered at the Designing For Digital 2019 conference.


