Post contributed by [Matthew] Farrell, Digital Records Archivist.
The Duke University Archives collects records documenting University history. We’ve done it for a long time, and we’d like to think we’re (pretty) good at it. While there are a lot of organizational, legal, and business-oriented reasons to preserve the records of Duke, a university isn’t really a university without the students who live, study, and work here. So in addition to the records documenting Duke’s administration, building and grounds, and athletics, we also collect materials documenting student life.
One of the biggest and best sources of such materials are student organizations (fun fact: there are over 800 organizations listed in DukeGroups !). We accept records in a large number of formats, but since I’m the digital records archivist, I’m going to focus on DIGITAL FORMATS.
We accept many, many types of digital stuff from all types of student organizations. Some examples:
- Arts organization Amandla Chorus donated video recordings of their dance performances.
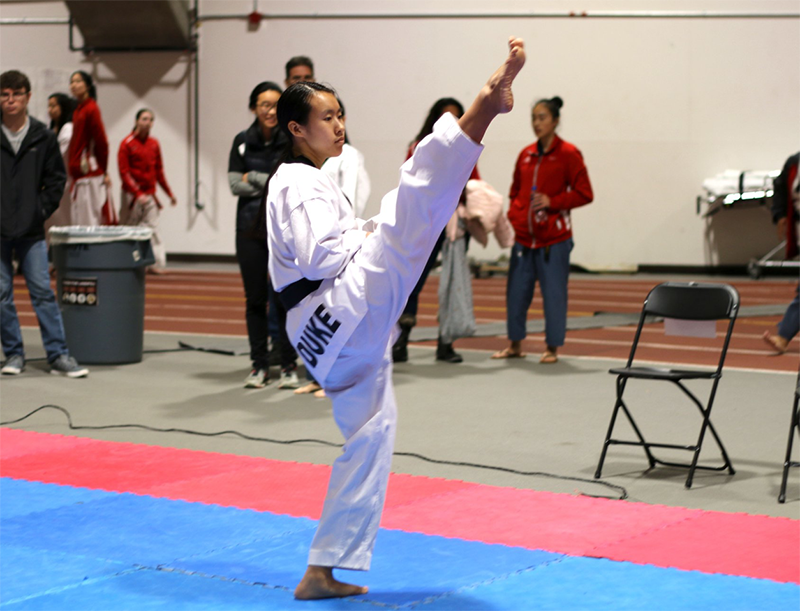
- Club Athletics organization Duke Taekwondo sent us digital photographs of their competitions.
- Political action organization Graduate Students Union donated document files in both MS Word and PDF regarding their struggle to gain official recognition as a labor union at Duke.
- Cultural organization Desarrolla asked us to crawl their website with our web archiving service.
- Social Justice organization Duke Students & Workers in Solidarity gave permission for us to harvest Tweets related to their occupation of the Allen Building in 2016.

We can work with your organization to identify the best way to get digital records to the Archives. Google Drive and Box are popular methods to transfer files to us from the Cloud. We can lend you a hard drive for files stored on local laptop or desktop computers. We can accept removable storage media of many different types (CDs, DVDs, thumb drives, ZIP disks, or Floppy disks). We have a whole website set up to give student organizations information about how to transfer materials to the Archives. We’ll consult with you to ensure that you’re sending us the records you want to send us, and not any sensitive material.
Bottom line: we want to make it as easy as possible for your organization to donate your records to our holdings, to ensure that the mark your group is currently making (or made if you’ve already graduated) enters the historical record, able to inspire future generations of Duke students.