Post contributed by Laurin Penland, Library Assistant for Rubenstein Technical Services
For someone like me who studied Joseph Conrad’s The Heart of Darkness in school, the Congo River can play an outsized role in my imagination as a place of brutal Western imperialism. So, you can imagine, how, when I was carefully paging through a diary from 1852 for a ship named the Mary Adeline, I froze in a moment of recognition upon seeing the words, “I was in the Congo River 12 days, during which time got ashore Shark’s Point. Was attacked by the savages, defended the vessel successfully and was eventually got off by … [the] steamer ‘Firefly’ and schooner ‘Dolphin.’”

This ship’s diary was written almost forty years before Conrad’s Heart of Darkness, during a time when enslavers were still abducting people from Africa and selling them if not legally, then illegally, especially to countries in South America (by that time many countries, including the US, had outlawed the transatlantic slave trade). The diary was kept by a man named Appleton Oaksmith—captain of the Mary Adeline—and though he does not mention enslaving people in the diary, I was suspicious. I wanted to know what he was doing in the Congo River and why he was “attacked.” So, I began to do more research.
First, I should provide a little more context. This diary was donated to the library as an addition to the Appleton Oaksmith papers, which the Rubenstein has held since 1937. The library had previously borrowed the diary in the 1950s so that it could be microfilmed. And now, decades later, the owners of the physical diary decided to donate it to the Rubenstein. It’s part of my job in the library to process new additions to collections, and this addition of the diary led me to try and discover what exactly the diary was about and how I might add it to the existing collection.
I did not know much about Oaksmith. In our online catalog, the description of Oaksmith stated merely that he was an “adventurer, author, ship owner, and industrial promoter of Hollywood, N.C.” A quick Google search for Oaksmith led me to think that “adventurer” was at best a polite euphemism and at worst a papering-over of the history of illegal slave trading. Here is one of the first entries I found about Oaksmith and his ship, the Mary Adeline:
“The U.S. brig Mary Adeline departed from Rio de Janeiro in April 1852 destined for the coast of Angola. After having been visited by the British steamship Fire Fly investigating evidence of slave trading, the Mary Adeline ran aground on a sandbar at Shark’s Point near the mouth of the Congo River. Within hours an estimated fifteen hundred to three thousand Africans attacked the boat. They used muskets, spears, oars, and cutlasses as weapons, along with hooks and poles to climb the side of the ship. The small crew of the Mary Adeline fought back by shooting a six-pound cannon that killed several of the Africans…. News of the battle spread quickly. Couriers capable of running fifty to sixty miles a day surely carried this information along the African coast. Inhabitants of Salvador learned of the attack after the return of the Mary Adeline to Salvador in late July. A planned attack by Africans of a slaving vessel helped to convince Bahians and foreigners resident in Salvador that a resumption of the slave trade would pose significant and unwanted risks.”[1]
This passage is from Dale Torston Graden’s monograph, From Slavery to Freedom in Brazil, Bahia, 1835-1900. Graden’s description of the battle in the Congo River suggests two important points: 1) It is likely that Oaksmith was attempting to enslave West Africans, and 2) the attack played a significant role in limiting or ending the slave trade in Brazil. If these things were true, why did previous archivists describe Oaksmith as an “adventurer” and not as an enslaver?
This question sent me searching our digitized collection of the Rubenstein’s old card catalog. This is often the first place I look when trying to find more information about collections that the library has held for a long time, given that sometimes, descriptions in the old card catalog were never migrated to the online catalog due to length, complexity, or outdated language. The old card files on Oaksmith included a long biographical sketch. The writer of the description chose to describe the battle on the Congo River through the lens of the crew members of the Dolphin who helped Oaksmith escape. According to the Dolphin, Oaksmith fought “gallantly” against “3000 natives who had assembled for the purpose of plundering [the Mary Adeline’s] valuable cargo.”[2] Later, the card file mentions that Oaksmith was indicted for slave trading, that he escaped from jail, and that he was eventually pardoned by President Grant. I was confused by the card file and by our online description, especially in juxtaposition to other scholarship that I found online. Was Oaksmith on the Congo River to enslave people? What was his valuable cargo? Why was he attacked? If he was eventually indicted, when was he convicted? How should I change the description of Oaksmith in the online catalog?

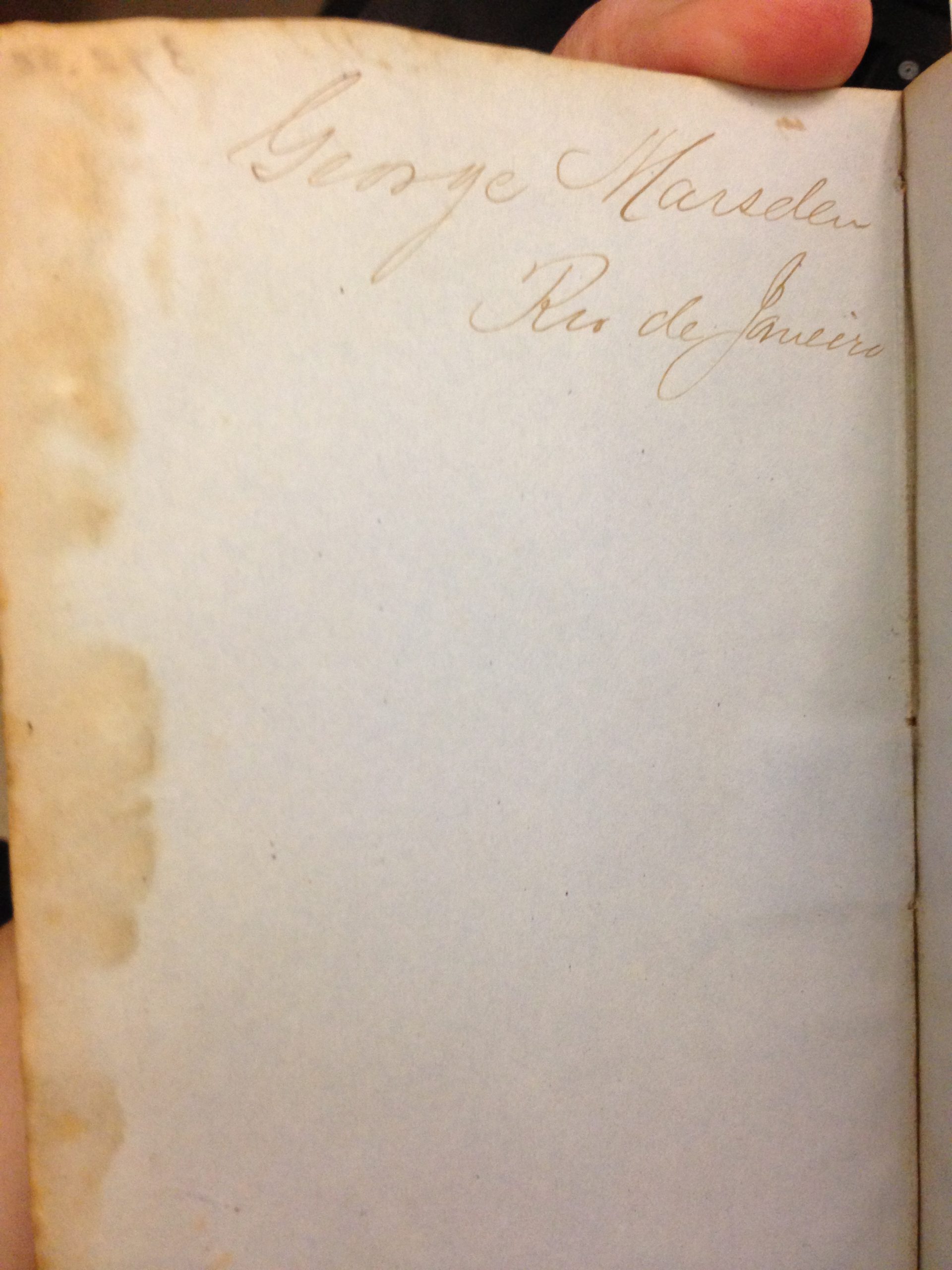
One curious aspect of the diary is that there is an inscription inside the front cover that reads, “George Marsden, Rio de Janeiro.” I found mention of Marsden in The United States and Transatlantic Slave Trade to the Americas, 1776-1867:
“[In 1852] the British Prime Minister to Brazil, Henry Southern, wrote to the foreign office about indications that the US vessels Mary Adeline and Camargo were being prepared to engage in the slave trade. ‘Mr. Marsden, a broker in Rio, a citizen of the United States,’ continued Southern, ‘is the party who is actively interested in getting up and aiding these speculations.’”
Later in 1852, the Camargo “disembarked 500 slaves at Bracuhy, south of Rio de Janeiro.”[3] Marsden was jailed but was eventually freed. The captain of the Camargo, Nathaniel Gordon, escaped from Brazil, but was hung ten years later in the United States for slave trading. (Gordon is the only person in US history to have been executed for the crime of slave trading; his conviction and hanging are largely credited to the politics of that moment with the start of the Civil War and the beginning of Lincoln’s presidency.) The last place that Gordon abducted West Africans was at Shark’s Point on the Congo River, the same place that Oaksmith had run aground years earlier.[4] And as for Marsden, after he was released from jail, he went on to be involved with a New York shipping company that was caught trafficking enslaved people to Cuba. Oaksmith also had significant ties to Cuba: his brother Sidney lived there, and Oaksmith himself was perhaps best known by historians as an ardent supporter of William Walker who “planned to establish a Central American empire that would ultimately include Spanish Cuba.”[5]

It turns out that there is a copious amount of scholarship on Oaksmith and the illegal slave traders of his time. While I have not yet determined with certainty the purpose of Oaksmith’s journey to the Congo River in 1852 aboard the Mary Adeline and the reasons for the battle that ensued, I found historical evidence for his later attempts at slave trading, thus justifying two changes in the collection description: mentioning in the online catalog that Oaksmith was indicted for outfitting the slave ship Augusta in 1861 and finally convicted for outfitting the slave ship Margaret Scott in 1862, and adding “Slave trade – United States – 19th century” as a subject heading. I also decided to remove the word “adventurer” from his biographical description, lest it glorify the horrors of the slave trade and chattel slavery. The Appleton Oaksmith papers have also been added to a list of collections to which Rubenstein archivists hope to return, down the road, so that we can provide more detailed and just description. This is one of many legacy collections at the Rubenstein that deserve to be reprocessed and re-described so that we can better document the history of slavery and redress archival errors, silences, omissions, and erasures.
As for the ship’s diary that inspired this blog post, it has finally joined the rest of Oaksmith’s papers at the Rubenstein Library and will be requestable in the reading room once the library has reopened.
[1] Dale Torston Graden, From Slavery to Freedom in Brazil, Bahia, 1835-1900 (Albuquerque: University of Mexico Press, 2006), 8.
[2] Card catalog entry for the Appleton Oaksmith Papers, David M. Rubenstein Rare Book & Manuscript Library.
[3] Leonardo Marques, The United States and Transatlantic Slave Trade to the Americas, 1776-1867 (New Haven & London: Yale University Press) 170, https://doi.org/10.12987/yale/9780300212419.001.0001.
[4] Ron Soodalter, “Hanging Captain Gordon.” Civil War Times, 08, 2009, 46-53.
[5] John J. TePaske, “Appleton Oaksmith, Filibuster Agent.” The North Carolina Historical Review 35, no. 4 (1958): 427-47. Accessed June 15, 2020. www.jstor.org/stable/23517266.


