Post contributed by Brooke Guthrie, Research Services Librarian
There’s no denying it: artifacts are more fun when they come with sharp blades! And, in the History of Medicine Collections, we have a lot of sharp things! From giant amputation saws (for your less precise cutting needs) to more modern surgical kits, it’s a wonder we still have all of our fingers!
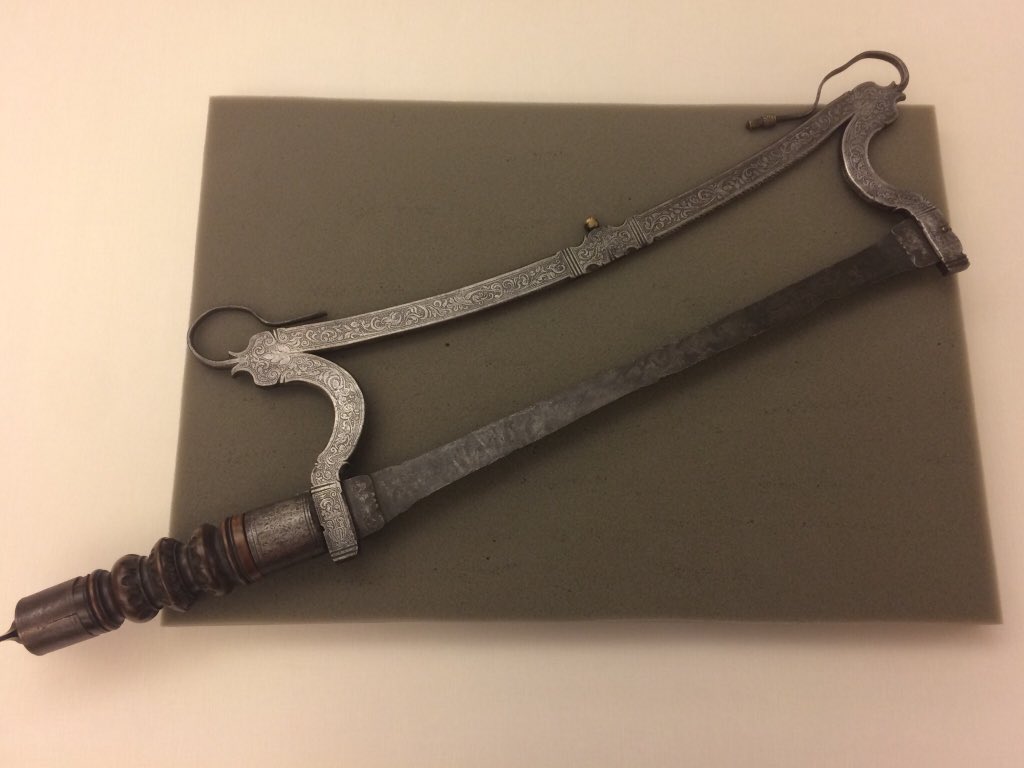

Not all of our blades are for such extreme procedures as amputations. We have many examples of smaller (but no less sharp) cutting tools intended for the once-popular procedure of bloodletting. Intended to balance the body’s humors and restore a patient to health, bloodletting was a standard medical procedure for centuries. Used to cure a range of ailments, bloodletting could involve draining a patient of large quantities of blood. Benjamin Rush, prominent physician and signer of the Declaration of Independence, recommended bloodletting as a treatment during the 1793 yellow fever outbreak in Philadelphia. [The Benjamin and Julia Stockton Rush papers, which document Rush’s medical work, have been digitized and are available online.]
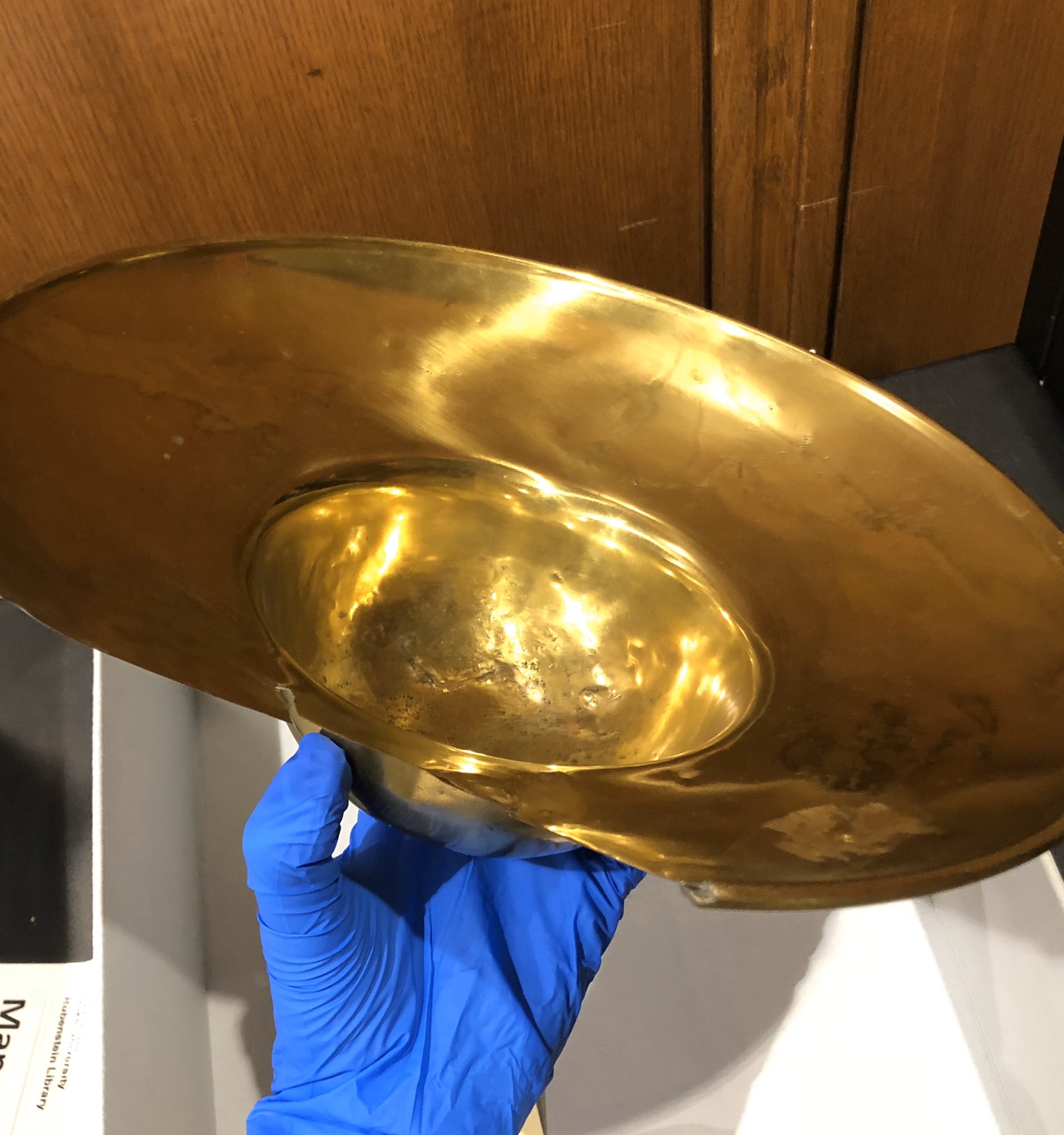
If, for some reason, you needed to bleed someone, you could choose from a number of tools in our collection like three-bladed fleams, lancets with tortoiseshell handles, and scarificators with as many as sixteen blades. We even have bleeding bowls to keep all of that blood from dripping onto your carpet. [Disclaimer: As appealing as it may sound, the Rubenstein Library does not recommend bloodletting. We recommend getting your medical advice from a medical professional and not a library blog.]

The many-bladed scarificator is an interesting device and we have several examples in our collection. Designed to create multiple cuts simultaneously, the narrow and quickly-delivered punctures produced by the scarificator made it a (supposedly) less painful bloodletting technique.
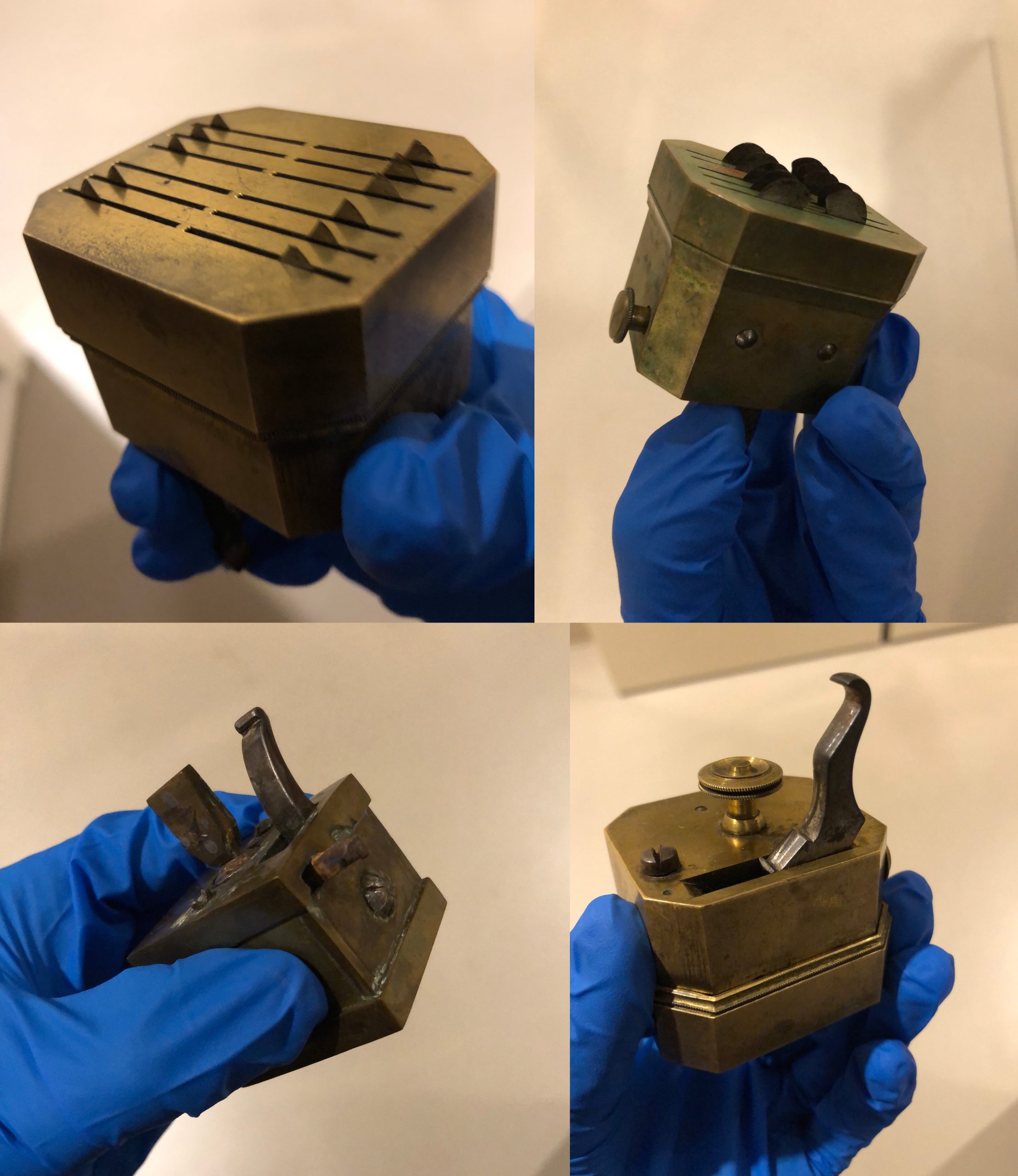

To use the scarificator, a doctor would retract the blades and cock them into position using the lever seen in the images above. The device would then be placed blade-side down on a patient’s arm and the button used to release the blades into the skin. [For an excellent demonstration, see this video from the Mütter Museum.]
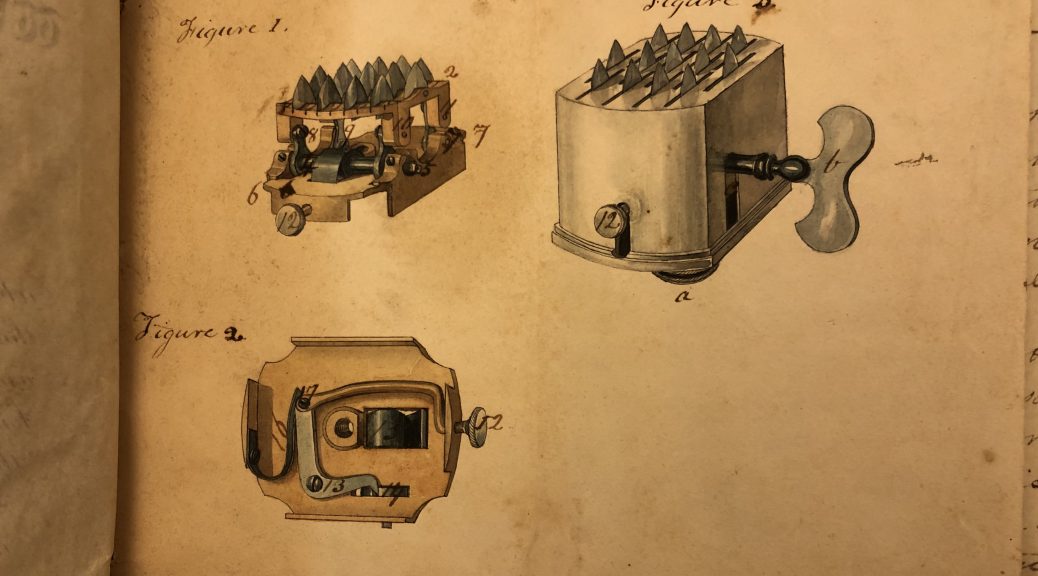
The frustrating thing about the scarificator is that the inner workings are hidden. What’s going on in that little brass box? As you might imagine, we prefer that people not pry apart our artifacts to find out. Luckily, other items in the History of Medicine Collections can fill in details about the design of medical instruments as well as the thought process behind the design.
A patent is one way to learn more and we hold a patent granted to George Tiemann in 1834 for a scarificator. The patent is an impressive document: it is signed by President Andrew Jackson and includes several hand drawn images of Tiemann’s device along with Tiemann’s very detailed description of how the device works and is constructed.


This is only a quick look at George Tiemann’s patent and we encourage further research into scarificators and other medical instruments (we have over 800 and many have been described and photographed). Maybe, if you are handy type of person, you could try to recreate Tiemann’s design!


This is very powerful device.
Since I discovered this website, I’ve been learning new things. Thanks for sharing this
It is genuinely good for the readers to go through something which is appealing and the instincts in mind get a boost. Hopefully, we will get to read more of this through similar posts.