After my recent dabbling in miniature book work, I felt it was only appropriate to switch things up and work on something large.
These two sizeable sets of East Asian books were exactly what I was looking for. Occasionally a set like this would be broken down into its individual books. However, since each set came with a unique cloth enclosure, they were cataloged as one whole item.
Therefore, I will treat each set as a single unit.
So, What is the Treatment?
I am glad that we are keeping the original enclosures, however it makes my job trickier. The current case doesn’t provide enough protection as it is. Even just a gentle push is enough to slide the books out of the enclosure, which could cause unwanted damage to the books in the set.
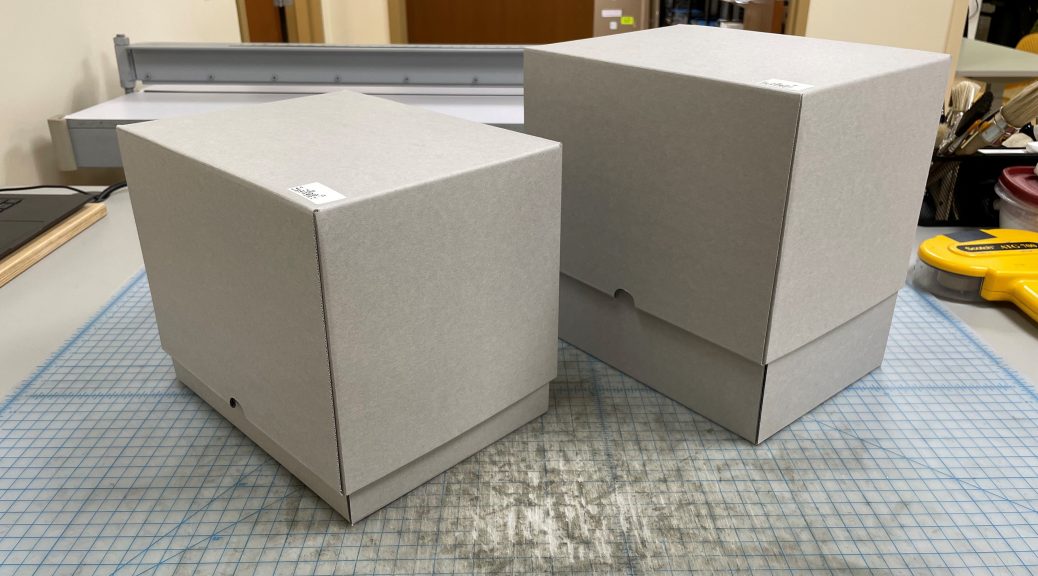
The best treatment option is to make each set a new box. That way the entire unit will be safer whenever it is transported or handled.
Normally this wouldn’t be anything new, but boxing something this tall is a first for me. The thickest books I’ve worked with were typically four or five inches thick as most. On the other hand, these two sets are a whopping nine and eleven inches tall.
Due to their size, a normal clamshell box is no longer an option. If I applied their dimensions to our usual clamshell design, the box would not fit on the sheets of E-Flute board that we have in the lab. The best solution to this problem is to make a telescoping box instead, which is made of two parts (an interior piece and a lid) instead of one.
How Do You Make Such a Large Box?
Even with this alternative design I had to make some adjustments. The book sets were large enough that they still didn’t quite fit on the boards. This meant I had to change how I transferred the design onto the board.

To make the majority of the box fit, I made all my measurements from the center line of the board edge. This method allows me to fit all the critical parts of the box on the board.
With all the important marks made I can now crease the board, make the necessary cuts, and assemble the interior piece of the box.
The lack of board is more apparent once the box is put together.
Luckily the solution is a simple one. All I need is a piece of scrap E-Flute (which we have plenty of) to fill the gap in the side wall.
Once that is complete, I made the lid of the box. I measured this piece the same way I did before in order to be as economical as possible with the board.
After that I just had to repeat the process for the second set of volumes.
Now these massive sets are ready to go! Too bad they’re still just as heavy though.